WHAT IS THE ENDOCANNABINOID SYSTEM?
Cannabis is a dynamic plant. With thousands of different strains and hundreds of active ingredients, cannabis offers a wide range of effects. Whether you’re trying to catch a buzz or tap into weed’s therapeutic benefits, there’s a cannabis product for you.
But have you ever wondered how the plant works in the body, or why it makes you feel the way it does?
It turns out that humans (and all mammals) are actually equipped with the tools it needs to process cannabis flower and other products. It’s called the endocannabinoid system (or ECS) and is the key to unlocking all that weed has to offer.
First discovered in 1988, the ECS doesn’t just play a big part in how cannabis strains make you feel. It also helps other parts of the body function properly.
Want to know more about the endocannabinoid system and its fascinating abilities? Read on for our deep dive.
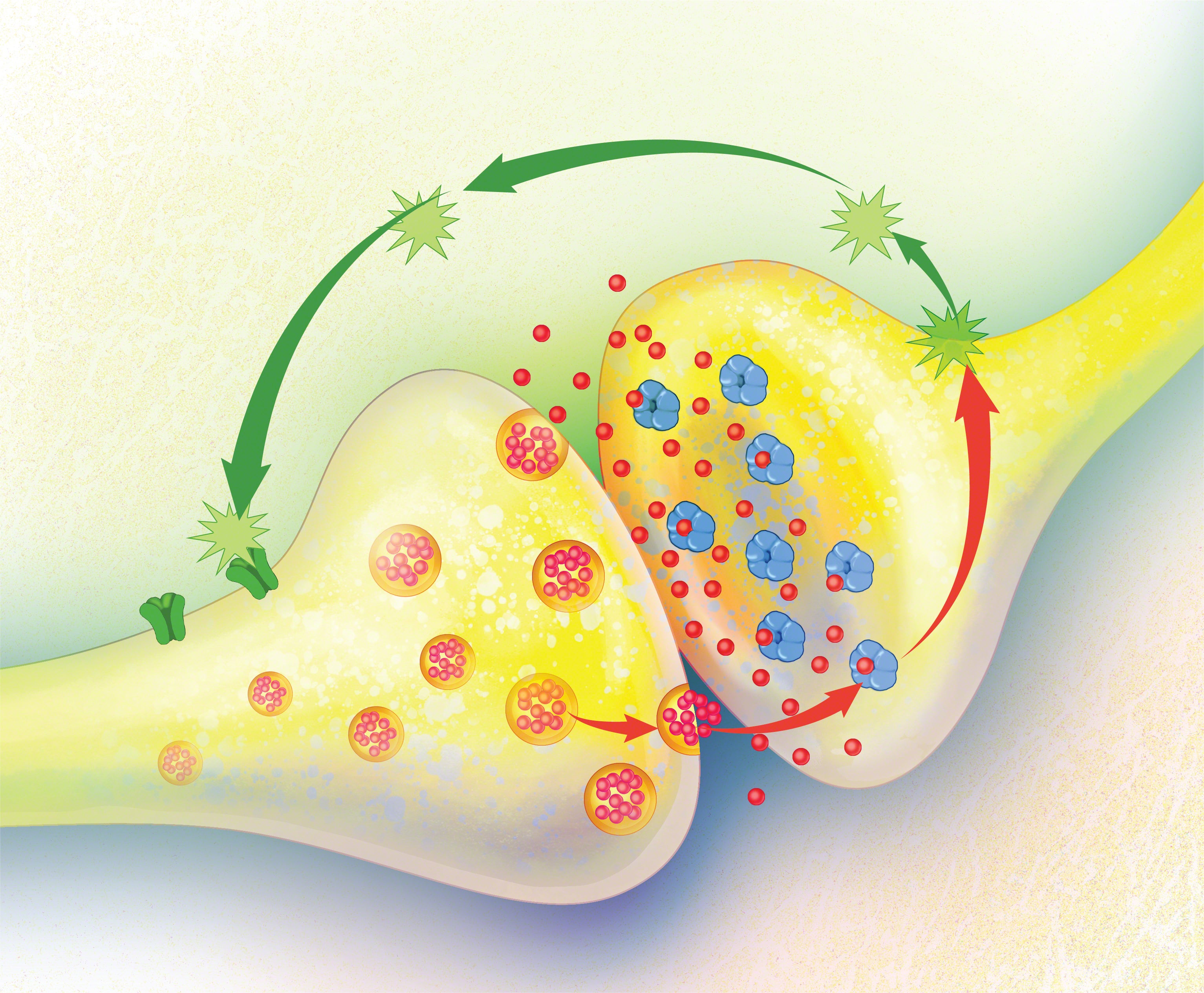
What is a cannabinoid?
Before we get into the ECS, it’s important to understand the molecules of cannabis flower at the center of it all.
Cannabinoids are a group of compounds mostly found in cannabis flower. They are sometimes referred to as phytocannabinoids, meaning they come from plants. Cannabinoids are the active ingredients responsible for the effects strains of weed offer.
The most famous phytocannabinoids are THC and CBD. However, there are over 100 others that have been identified. These lesser-known cannabinoids are starting to pop up in dispensaries, and include CBN, CBG, CBC, and THC-V.
Animals and humans also make their own cannabinoids, typically called endocannabinoids. The “endo” root indicates they come from within.
Endocannabinoids are enzymes that act as messengers between cells. They are typically activated when the ECS is triggered but may also be responsible for the euphoric “runner’s high” people experience after a robust workout.

The Endocannabinoid System Explained
While little is known about the ECS in the eyes of the scientific community, more is being discovered every day.
We do know the endocannabinoid system is a part of the central nervous system. It’s responsible for maintaining harmony within the body. The Medical Cannabis Handbook refers to it as “the chemical bridge between body and mind.”
Let’s explore what else has been revealed about the ECS so far.
The ECS is a vast network
The endocannabinoid system consists of a large network of receptors throughout the body. They are known as CB1 and CB2 receptors.
CB1 receptors are mostly found in the brain. Researchers at Harvard liken them to traffic cops, helping to regulate the activity of other neurotransmitters.
CB2 receptors typically exist in the body’s immune tissues and help control immune system function including inflammation. This may explain why so many cannabinoids have anti-inflammatory properties.
Unlike CB1 receptors, the CB2 receptors do not modulate the “high” we feel when we consume THC.
This makes CB2 especially intriguing for scientists and healthcare professionals hoping to capitalize on the potential wellness benefits of cannabinoids.
Endocannabinoids that our bodies naturally produce, like the enzyme anandamide (aka the bliss molecule), stimulate CB1 and CB2 receptors. When we consume cannabis, phytocannabinoids like THC or CBD take over the system leading to any psychoactive effects they may provide.

The ECS is essential to every life
The endocannabinoid system is crucial for human survival. It’s a “master regulator,” helping to maintain homeostasis in the body. This means it ensures every organ, cell, and system works the way it should. If we didn’t have the ECS, we wouldn’t be able to eat, sleep, or reproduce.
The ECS kicks into high gear when systems are threatened. For example, if you fall over and break a bone, the ECS will send signals to the affected area causing you to experience swelling and feel pain. This tells the body to beware, protecting it from further injury.
The ECS plays a role in memory and learning
In addition to regulating the brain, the endocannabinoid system is also believed to affect how well we remember and retain information. It is believed that the ECS helps us learn new facts due to its regulation of neural transmissions (ie, activity in the brain).
THC has been shown to have an effect on memory, specifically CB1 activation. It is theorized that this activity makes cannabis an effective tool in the fight against post-traumatic stress disorder.
Famed botanist Michael Pollan once wrote that the co-evolution of the cannabis plant alongside mankind specifically to help us forget in order to help us thrive. He hypothesized that sensory overload could lead to the brain malfunctioning and that cannabis helps reduce that overload.

The ECS could alter our moods
With so many CB1 receptors in the brain, it may also factor into how we feel emotionally.
One 2009 study showed the endocannabinoid system may help regulate mood, including depression and anxiety. Scientists believe stimulating CB1 receptors with certain cannabis strains could lead to future treatments for mental health disorders.
The ECS may affect appetite
The scientists at Harvard exploring the endocannabinoid system also ponder if it could control hunger and aid in weight loss.
Researchers theorize the ECS, specifically CB1 receptors, regulate appetite. This would make sense since THC tends to make people want to eat. THC-V has been shown to decrease cravings and could be a part of anti-diabetes treatments in the future.

Could a lack of cannabinoids lead to illness?
Studies on the ECS have led scientists to explore whether a lack of naturally-occurring cannabinoids may be a factor in some health conditions.
A 2016 article by well-known cannabinoid researcher Dr. Ethan Russo drew attention to something called clinical endocannabinoid deficiency.
He suggested that migraines, fibromyalgia, irritable bowel syndrome, and certain neurological issues could be partially caused by too few naturally-occurring endocannabinoids.
The theory is definitely intriguing and is more evidence for the efficacy of medical marijuana for these conditions.
The ECS and the Entourage Effect
It turns out that cannabinoids aren’t the only compounds processed in the ECS.
The cannabinoids in different cannabis strains join other active ingredients such as terpenes in the plant to give you the full effects thanks to something called the entourage effect.
This is the theory that these chemicals have a special synergy that makes one another work even better. A small number of studies support the concept, including one 2011 paper that showed cannabis-derived terpene myrcene has more anti-inflammatory abilities when alongside THC and CBD.

How different strains of cannabis flower affect the ECS
As we briefly explored earlier, cannabis strains can have a wide range of effects based on the cannabinoids and terpenes present as they stimulate the ECS in different ways.
For example, weed strains that have a lot of beta-caryophyllene (a peppery terpene) tend to bind to the CB2 receptors. This means they may have more of an anti-inflammatory effect.
Strains that are high in CBD may enhance the abilities of the ECS. Research shows that cannabinoid may help strengthen the health of naturally-occurring endocannabinoids.
Finding the best strains of weed for your unique needs depends on your desired outcomes and your individual endocannabinoid system. Everybody is built differently, so some trial and error may be necessary before you dial in your cannabis regimen.
At STIIIZY, we only use premium flower for all of our 40's pre-rolls (40% THC potency) and high quality pre-rolls. Explore all of STIIIZY’s products here.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
Sources cited:
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1760722/
- https://www.nytimes.com/2021/03/10/well/move/running-exercise-mental-effects.html
- https://connect.springerpub.com/content/book/978-0-8261-3573-5
- https://www.health.harvard.edu/blog/the-endocannabinoid-system-essential-and-mysterious-202108112569
- https://www.jyi.org/2018-june/2018/6/1/the-endocannabinoid-system-our-universal-regulator
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0006322321014724
- https://michaelpollan.com/books/the-botany-of-desire/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3808114/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5576607/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3165946/
- https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.0803601105
- https://www.projectcbd.org/cbd-endocannabinoid-system
The content provided on this blog is for informational purposes only and is not intended as professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Please consult with your healthcare provider and local laws before purchasing or consuming cannabis.

